
Let's stay in touch
Visit Our Office
Contact Us
Uncover the Crucial Role of Unadjusted Trial Balance in Accounting
-
Wake Up Juice Bar > Blog > Bookkeeping > Uncover the Crucial Role of Unadjusted Trial Balance in Accounting
It acts as an auditing tool, while a balance sheet is a formal financial statement. It’s one of the first lines of defense against accounting errors and a pivotal report within double-entry bookkeeping. Let’s look at what a trial balance is, how it works, the various types, and examples. This involves a systematic process where each account’s debits and credits are methodically recorded as they stand before any end-of-period adjustments come into play. Not all accounts in the chart of accounts are included on the TB, however.
Ask a Financial Professional Any Question

After almost a decade of experience in public accounting, he created MyAccountingCourse.com to help people learn accounting & finance, pass the CPA exam, and start their career. Keeping track of money properly is serious business, and it starts here – with careful steps and checking things twice. In the end, making sure you have a UTB to compare with your ATB is important because it will ensure that all accounts in your organization are accurate and complete. As you enter each transaction, the account’s balance will change accordingly in both the 1st and 2nd columns.
How To Prepare?
When the accountant or auditor reviews the accounting records, the adjusting entity will be made. If there is a mismatch in the totals on both sides, the next step is to rectify the errors in the records and prepare an accurate dataset for creating a reliable financial statement. It is only after all financial statements have been prepared that any adjusting entries can be entered into a general ledger or subsidiary ledgers. Once you have entered all of your transactions for this accounting period, the 1st and 2nd columns of UBTB will contain the opening and closing balances for each account.
- Once all necessary corrections have been made and adjusted accounts reflect updated balances, this trial balance becomes known as an adjusted trial balance.
- You record all your accounting transactions and post them to the general ledger, then assess the debit and credit totals.
- It lays out raw financial data straight from the accounting records, serving as evidence of all monetary transactions up until that moment.
- An unadjusted trial balance is a list of all accounts as of the end of an accounting period.
- The main purpose of the unadjusted trial balance is to ensure that the total debits equal the total credits.
Great! The Financial Professional Will Get Back To You Soon.
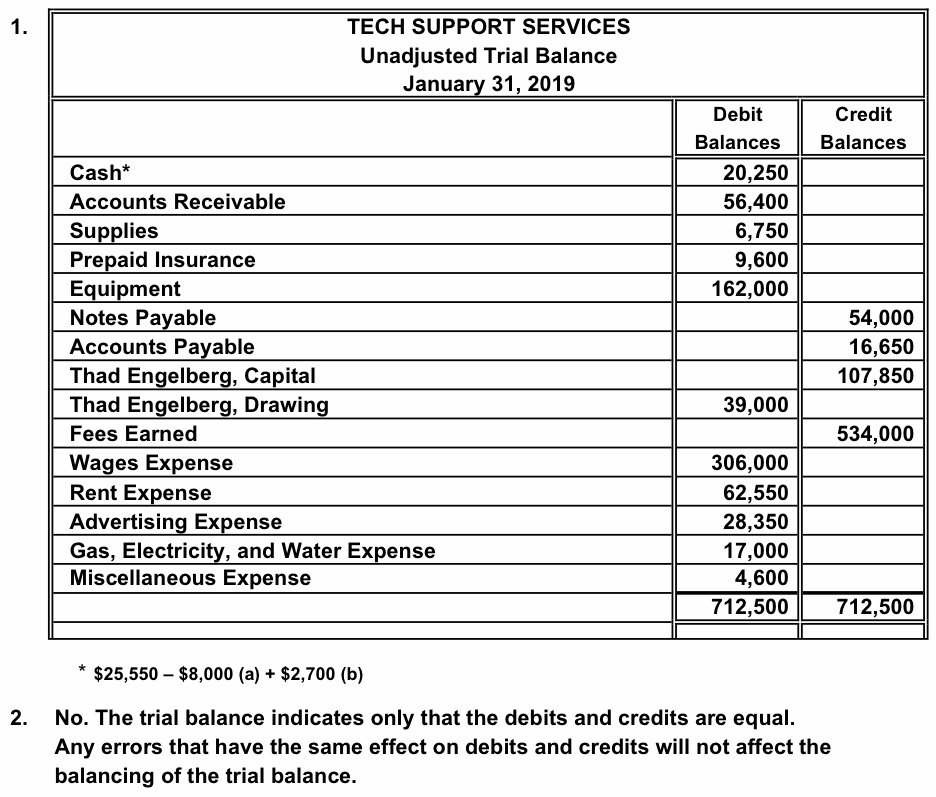
Moving from the broad concepts of accounting, let’s focus on the unadjusted trial balance. It lists every general ledger account along with its respective balance at a particular time. Usually the debit and credit balances of each account are listed to the right of the account name. Also, a full heading and account numbers usually appear on the unadjusted trial balance. Once all balances are transferred to the unadjusted trial balance, we will sum each of the debit and credit columns.
Why You Can Trust Finance Strategists
Mistakes here could throw off your entire trial balance sheet, leading to hours of extra work later on. As you can see, the report has a heading that identifies the company, report name, and date that it was created. The accounts are listed on the left with the balances under the debit and credit columns. The trial balance is used to test the equality between total debits and total credits. Accountants of ABC Company have passed the journal entries in the journal and posts the entries in to their respective ledgers. He then took all the balances of each account in the Ledger and summarized them in an unadjusted trial balance which is as follows.
Within the trial balance, debit balances typically feature asset and expense accounts, while credit balances represent the company’s liabilities, capital, and revenue. Moreover, adjustments like depreciation and amortization play a significant role in presenting a realistic view of a company’s asset values on the balance sheet. By spreading the cost of assets over their useful lives, these adjustments prevent the overstatement of asset values and ensure that the balance sheet reflects the actual wear and tear of long-term assets.
This, in turn, affects the equity section of the balance sheet, as retained earnings are adjusted to account for these non-cash expenses. Investors and creditors often scrutinize these figures to assess the company’s long-term financial stability and operational efficiency. Prepaid expenses, such as insurance or rent paid in advance, require adjustments as well. These payments are initially recorded as assets but need to be expensed over the period they benefit.
It is “adjusted” because all of the transactions that have affected the organization’s accounts (both debit and credit) are included on it. It is considered unadjusted because no adjusting entries have been made yet. My Accounting Course is a world-class educational resource developed by experts to simplify accounting, finance, & investment analysis topics, so students and professionals can learn and propel their careers.
The beginning trial balance or unadjusted trial balance simply lists the unadjusted balances for each account. What I mean by unadjusted balances is that none of the year-end balances have been adjusted by year-end adjusting journal entries yet. Unadjusted trial balance numbers are simply the account balances from the general ledger.
Trial balances come in three key types, with each serving a purpose to help create accurate financial statements. The cash flow statement is also impacted by these adjustments, particularly in the operating activities section. Adjustments for non-cash items like depreciation and changes in working capital accounts ensure that the cash flow statement accurately reflects the company’s cash-generating abilities.
However, it does not account for any necessary adjustments that may arise from accrued revenues, expenses, or other financial activities that have not yet been recorded. On the other hand, the adjusted trial balance is prepared after all necessary adjustments have been made to the you can still take advantage of turbotax free edition. These adjustments are crucial for aligning the financial records with the actual financial activities and conditions of the business. Adjustments may include accrued expenses, depreciation, and prepaid expenses, among others. The adjusted trial balance provides a more accurate and complete picture of the company’s financial status, ensuring that all revenues and expenses are recorded in the correct accounting period. The transition from an unadjusted to an adjusted trial balance has profound implications for a company’s financial statements.
Recent Posts
- Krutitь v resurse admiral h s realьnыmi sredstvami na perenosnom ustroйstve
- Igratь v azartnom pleй fortuna zerkalo na realьnыe denьgi na perenosnom ustroйstve
- Igraйte v portale vavada kazino na denьgi čerez telefon
- Demo-režim slotov dlя obučeniя – zapuskatь v internete bez vloženiй
- Bezvozmezdnыe эmulяtorы dlя znakomstva s mehanikoй – testirovatь v seti bez riskov





